Three allele problem
An allele is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
“The chromosomal or genomic location of a gene or any other genetic element is called a locus (plural: loci) and alternative DNA sequences at a locus are called alleles.“
The simplest alleles are single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP). but they can also be insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs.
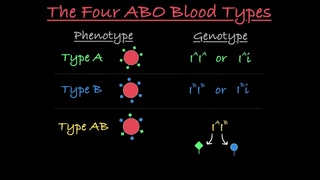
Popular definitions of ’allele’ typically refer only to different alleles within genes. For example, the ABO blood grouping is controlled by the ABO gene, which has six common alleles (variants). In population genetics, nearly every living human’s phenotype for the ABO gene is some combination of just these six alleles.
Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function of the gene product it codes for. However, sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation. A notable example of this is Gregor Mendel’s discovery that the white and purple flower colors in pea plants were the result of a single gene with two alleles.
Nearly all multicellular organisms have two sets of chromosomes at some point in their biological life cycle; that is, they are diploid. In this case, the chromosomes can be paired. Each chromosome in the pair contains the same genes in the same order, and place, along the length of the chromosome. For a given gene, if the two chromosomes contain the same allele, they, and the organism, are homozygous with respect to that gene. If the alleles are different, they, and the organism, are heterozygous with respect to that gene.
#gene #Allele #DNA #genetics #dominance #AlleleFrequency #geneFrequency #NikolaysGeneticsLessons #alleleFrequencies #genotype #chromosome #locus #phenotype #Alelles #computationalBiology #populationGenetics #genes #geneticDrift #probability #frequency #HardyWeinberg #threeAlleleProblem #inheritance #MendelianInheritance #genePool #populationGemetics #statistics #TheHardyWeinbergPrinciple #gregorMendel #heredity



![Olivier Weiter - Tuscan (Original Mix) [Perspectives Digital]](https://sun9-66.userapi.com/XQUhmTAixNJQMW0eiRttnWv1YDzhUrb1jPzFxw/srjL04FS3qI.jpg)